When it comes to maintenance and construction work, scaffolding is necessary. Scaffolding provides a stable working surface for maintenance and construction workers. Scaffolding that is of poor quality could lead to accidents such as a fall or a collapse. Consequently, following proper safety rules is necessary to help minimize accidents and to safeguard your undertaking. Our blog will discuss and describe the various types of scaffolding employed by contractors, describe some of the necessary safety precautions to observe while operating on scaffolding, and how to meet the expectations of OSHA. Additionally, we will highlight the need to put the safety of your scaffolding above any other issue just to reduce the potential loss of life, expenses, and time on your project.
Basic Safety Rules For Scaffolding
Scaffolding is safer to work on if the following scaffolding safety precautions are followed. These important safety precautions provide a safe working environment and prevent accidents from occurring. Here are the most important basic scaffolding regulations every worker and supervisor should follow:

• Inspect the Scaffolding
- Inspect scaffold equipment for damage or missing parts before each use. Repair damaged or replace missing components prior to work.
• Be Sure That Workers are Trained
- All workers using scaffolding must be trained in scaffold hazards. This is an OSHA requirement.
• Personal Protective Equipment
- Hard hats, non-skid footwear, and fall protection equipment should be used by all workers on or around a scaffold.
• Never Exceed Load Limits
- Never allow the load limit to be exceeded. Doing so could cause the scaffold to collapse.
• Keep the Scaffold Clean
- Do not let trash or debris build up on the scaffold. This is a huge tripping hazard everyone who uses the scaffold.
Avoid Moving Scaffolding with Workers On It
- Stationary Setup: Moveable scaffolds like rolling towers must be stationary and secured before workers get on.
- Check Surroundings: Always check for power lines, equipment, or other hazards when repositioning scaffolds.
- Remove Materials: Ensure no tools or materials are left on platforms while the scaffold is moved, reducing the risk of items falling.
Follow Electrical Safety Guidelines
- Maintain Safe Distance: Scaffolds should be set up at least 10 feet (3 meters) away from power lines or electrical sources.
- Non-Conductive Materials: When working near power lines, use scaffolding and tools made of non-conductive materials like fiberglass or plastic to avoid electrical hazards.
- Ground Fault Protection: Use ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) for any powered equipment on or around scaffolding.
Implement Emergency Preparedness
- Emergency Equipment: Ensure that emergency equipment, such as fire extinguishers or first aid kits, is available and accessible on-site.
- Rescue Plan: Develop a fall protection and rescue plan that outlines emergency procedures for fallen or injured workers.
- Communication: Establish clear communication channels for emergency situations, allowing workers to quickly report incidents or request assistance.
Erecting Scaffolding Regulations
Failing to properly erect scaffolding may result in danger of collapse and potential injury. Because of this, the assembly of scaffolding, regardless of the height is subject to established safety regulations. Be sure to implement the following while assembling scaffolding:

- Use a secure and reliable base: The legs of the scaffold must be on or attached to a solid and level surface. Some supports may require the use of a baseplate or even mudsills for unsteady or soft surfaces. Under no circumstances should a scaffold base rest upon unstable objects, such as bricks, concrete blocks or barrels, to stabilize its legs.
- Properly brace the structure: Diagonal and horizontal braces must be used at intervals that are closer together the higher the scaffold extends. Every locking mechanism must be engaged and the scaffold must not be moved when workers are present.
- The height-to-base ratio: OSHA requires that the height to base width ratio be 4:1. If it is larger than that, the scaffold may need to be braced or tied to the structure.
- Install guard and toe rails: Guardrails are required on the platform or platforms that are at a height of 10 feet or more. Toeboards must be in place to prevent tools and other material from falling.
- Install extenders or outriggers: To increase stability, you may need to add outriggers or extenders to the rolling scaffolds or to the base of any scaffold that falls within the height to base ratio.
Worksite Safety Tips For Scaffolding
Once scaffolding has been erected, safety on the worksite is critical to avoid accidents. Regardless of how well the scaffold is constructed, an unsafe practice on the job site can create hazards. Below you will see some important Scaffolding rules and regulations for the job site which all workers and supervisors should adopt:
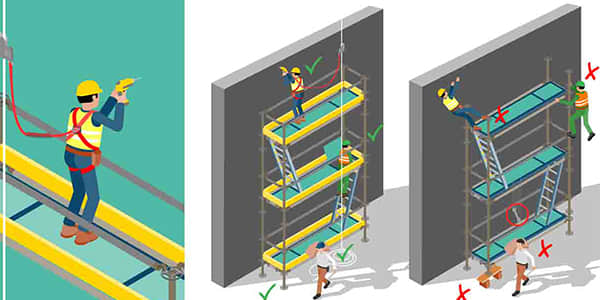
Maintain clearance from power lines:
- It is a requirement by OSHA to keep scaffolds at least 10 feet from any overhead power lines. If workers cannot keep clear of power lines or 10 feet cannot be maintained, then the power should be turned off or an electrical barrier should be installed to protect against shocks.
Prevent falls:
- Aside from guardrails on the scaffolds greater than 10 feet in height, any worker must use a personal fall arrest system (PFAS) when working at height on a scaffold. This may include harnesses and lanyards when working on suspended or raised platforms.
Avoid overloading the scaffold:
- A scaffold's load can consist of too many workers, tools, or materials, which will collapse the scaffold. Work with the max imposed load marked for the scaffold, and pay attention to weight distribution of the materials on the scaffold.
Secure tools and material:
- Tools and materials should be secured when not in use to prevent them from falling. Workers should secure tools to their body with a lanyard or tool belt, never leave tools laying on the scaffold site, and other than tool storage, materials shouldn't be left on the scaffold when not in use.
Use ladders and stairs properly:
- Workers should never use scaffold cross braces to climb up, nor should they use any unsafe method to get on or off the raised scaffolding. One should also avoid carrying tools or material when getting off or on a scaffold.
Weather Awareness:
- Weather conditions such as winds, rain, ice, or snow can create slippery conditions while on the scaffold, or they may simply be controlling if the work can be achieved at height.
Emergency Protocols For Scaffolding
Accidents can happen on scaffolding sites, so having clear emergency protocols is vital. Key protocols include:

- Emergency Action Plan (EAP): Create an EAP detailing evacuation routes, contact info for emergency services, and roles for key personnel. Conduct regular drills and ensure the plan is accessible to all workers.
- Response to Falls: In case of a fall, avoid moving the injured worker unless necessary. Call emergency medical services (EMS) and provide first aid if trained. If the worker is suspended, stabilize them but don’t put yourself at risk.
- Scaffold Collapse: Evacuate the area immediately and call emergency services. Account for all workers to ensure no one is trapped, using a communication system like a headcount.
- Electrical Emergencies: Do not touch the scaffold until power is de-energized. Report the issue to the utility company. If electrocution occurs, call EMS and administer CPR if safe.
- Rescue from Suspended Scaffolds: Call for rescue services if workers are stranded. Ensure they have personal fall arrest systems (PFAS) for emergency descent.
- Fire or Explosion: Evacuate using escape routes, activate fire alarms, and contact the fire department. Only use fire extinguishers for small, contained fires.
- Emergency Communication: Ensure workers have communication devices and appoint an emergency coordinator to direct responses. Use clear signals to alert others.
- First Aid Kits: Keep first aid kits stocked and accessible. Ensure at least one worker is trained in first aid and CPR.
- Post-Incident Procedures: Document the incident thoroughly, investigate causes, and provide support to affected workers.
In conclusion, while scaffolding is vital for construction projects, it poses significant safety risks. Adhering to safety guidelines, following OSHA regulations, and implementing effective emergency protocols can create a safer work environment and minimize accidents. Key practices like regular inspections, proper training, using personal protective equipment, and respecting load capacities are crucial in preventing falls and collapses. Scaffold safety is a collective responsibility of workers, supervisors, and employers, and prioritizing it ensures a smooth project flow without costly delays. Maintaining vigilance, effective communication, and best safety practices is essential for a productive worksite.
FAQ
What are the most common scaffolding hazards?
- Falls, scaffold collapses, electrical hazards, and falling objects are the most common risks associated with scaffolding.
How can falls from scaffolds be prevented?
- Falls can be prevented by installing proper guardrails, using personal fall arrest systems (PFAS), and ensuring workers are properly trained in fall protection.
What is OSHA's height requirement for fall protection on scaffolds?
- OSHA requires fall protection (guardrails or PFAS) for scaffolds that are 10 feet or more above the ground.
Get More Information
Scaffolding Safety Tips---TDI
A Guide To Scaffold Use---OSHA



